Hardware diagram of the wearable device Circuit Diagram The explosive growth of wearable technology and ubiquitous computing has revolutionized how we interact with electronic devices. This transformation has brought unique challenges and opportunities in printed circuit board (PCB) design and manufacturing. This comprehensive guide explores the essential aspects of designing PCBs for wearables and ubiquitous computing applications, focusing on

Wearable Electronics Our industry experience — combined with our state-of-the-art technology and advanced materials — makes us the perfect choice for your next wearable electronics PCB project. We also have extensive experience with the concept of miniaturization and will work with you from the initial design of a project through to the

Innovations in PCB Design for Wearable Technology Circuit Diagram
PCB design. The realization of the electronic circuit of a wearable is not limited to the PCB, but includes other materials such as fabric, plastic, rigid-flex boards, and mesh. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, flex and rigid-flex printed circuit boards are more durable and offer greater resistance to heat, humidity, weather and vibration Read the Altium Ebook on wearable electronics and PCB Design. Until recently, wearable accessories had one primary purpose-- to be fashionable. Sure, watches are useful for keeping time and staying punctual, but that's about as far as things went for functionality. Today, we have a rising selection of wearable electronics, many of which can be

Developing a wearable electronic product involves juggling design constraints and compromises in ways that are quite different from more conventional designs. This article discusses the main design tradeoffs for wearable technology products. Putting all the components together will commonly require multiple thin-substrate PCB's that are
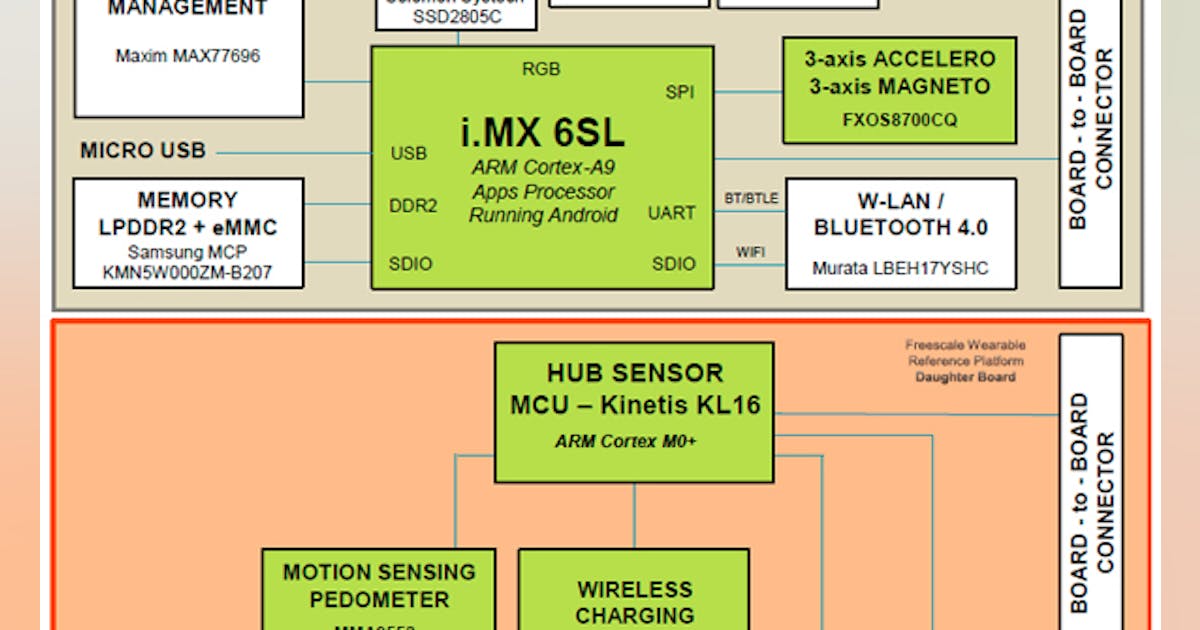
Design Notes for Wearable PCB Design Circuit Diagram
Normally, layer count varies from four to eight layers for wearable devices. Layer structuring is such that if it's an eight layer PCB, it provides enough ground and power plane to sandwich the routing layers. Thus, the ripple effect in crosstalk is kept to a minimum and electromagnetic interference or EMI is significantly reduced. Solutions from Molex include Quad-Row Connectors that save up to 30% of PCB space, IP67/68/69-rated interconnects for durability and advanced designs to prevent damage during assembly and use. Flexible floating connectors and compact layouts provide design versatility, while robust performance supports seamless integration of advanced features.
